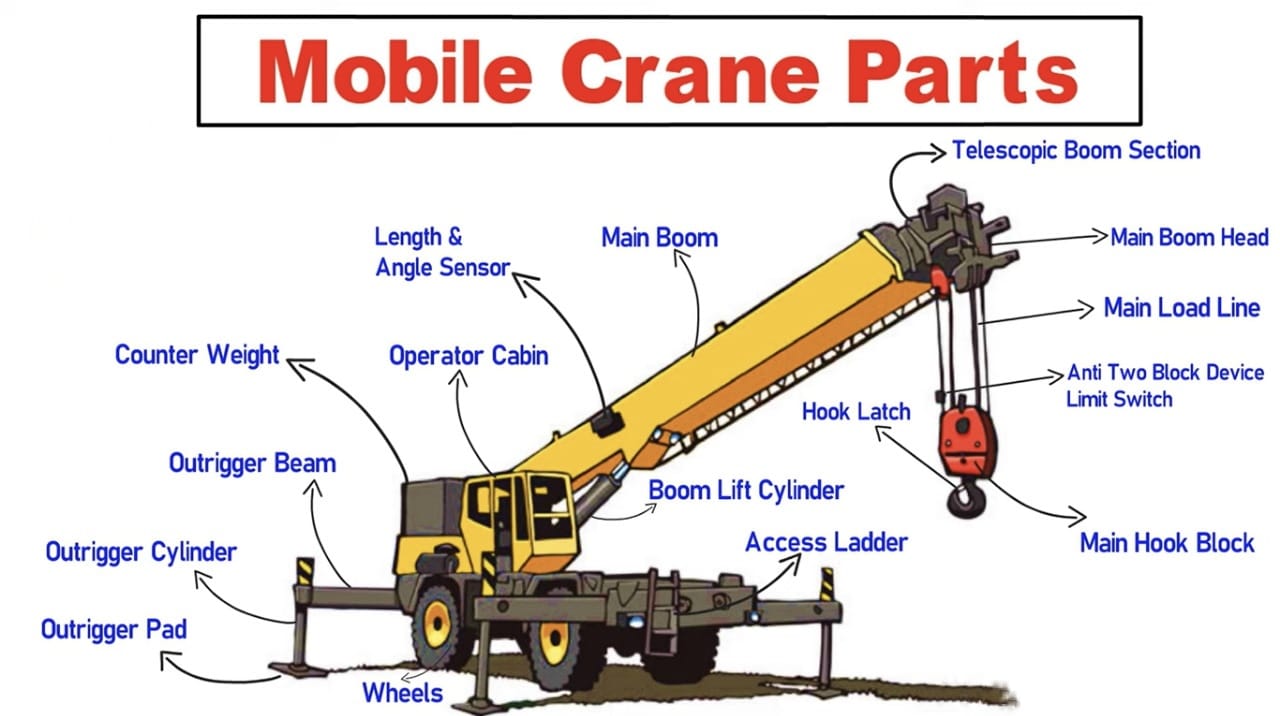
Mobile cranes are versatile lifting devices mounted on mobile platforms, enabling them to be transported to various locations as needed. They are commonly used in construction, manufacturing, and transportation industries for moving and lifting heavy items.
Overview of the parts of a mobile crane and their functions:
1. Telescopic Boom Section: This is the extendable part of the main boom that allows the crane to reach varying heights. It adjusts in length to handle different lifting requirements.
2. Main Boom Head: This component is located at the top of the main boom and serves as the attachment point for rigging and lifting gear.
3. Main Load Line: This is the primary cable or rope used for lifting loads. It runs from the winch through the boom and over the sheaves at the boom head.
4. Anti Two Block Device Limit Switch: A safety device that prevents the hook block from colliding with the boom tip. It stops the main load line from being retracted too far
5. Main Hook Block: This is the large, typically multi-sheaved component at the end of the load line. It allows for multiple line configurations to increase lifting capacity.
6. Hook Latch: A safety latch that prevents the load from slipping off the hook unintentionally.
7. Access Ladder: Provides safe access for operators to climb up to and from the operator cabin or other service areas on the crane.
Also Read: HOW HVAC AND HVDC DIFFERES EACH OTHER? DETAILED ANALYSIS
8. Main Boom: The primary lifting component of the crane, to which the telescopic section is attached. It supports the main load line and is crucial for the crane’s operation.
9. Boom Lift Cylinder: A hydraulic cylinder used to raise or lower the boom, allowing the crane to adjust the angle of lift.
10. Operator Cabin: The control center where the operator manages the crane’s movements and lifting operations.
11. Length and Angle Sensor: Sensors that provide real-time data on the boom’s extension length and angle, important for calculating lifting capacities and maintaining stability.
12. Counterweight: Weights mounted on the crane’s rear to balance the load being lifted and enhance stability.
13. Outrigger Beam: Extendable beams that increase the crane’s base and stabilize it during operations, particularly when lifting heavy loads.
14. Outrigger Cylinder: Hydraulic cylinders used to extend or retract the outrigger beams.
15. Outrigger Pad: Pads placed at the ends of the outrigger beams to distribute the crane’s load over a larger area, preventing overloading of the surface beneath and enhancing stability.
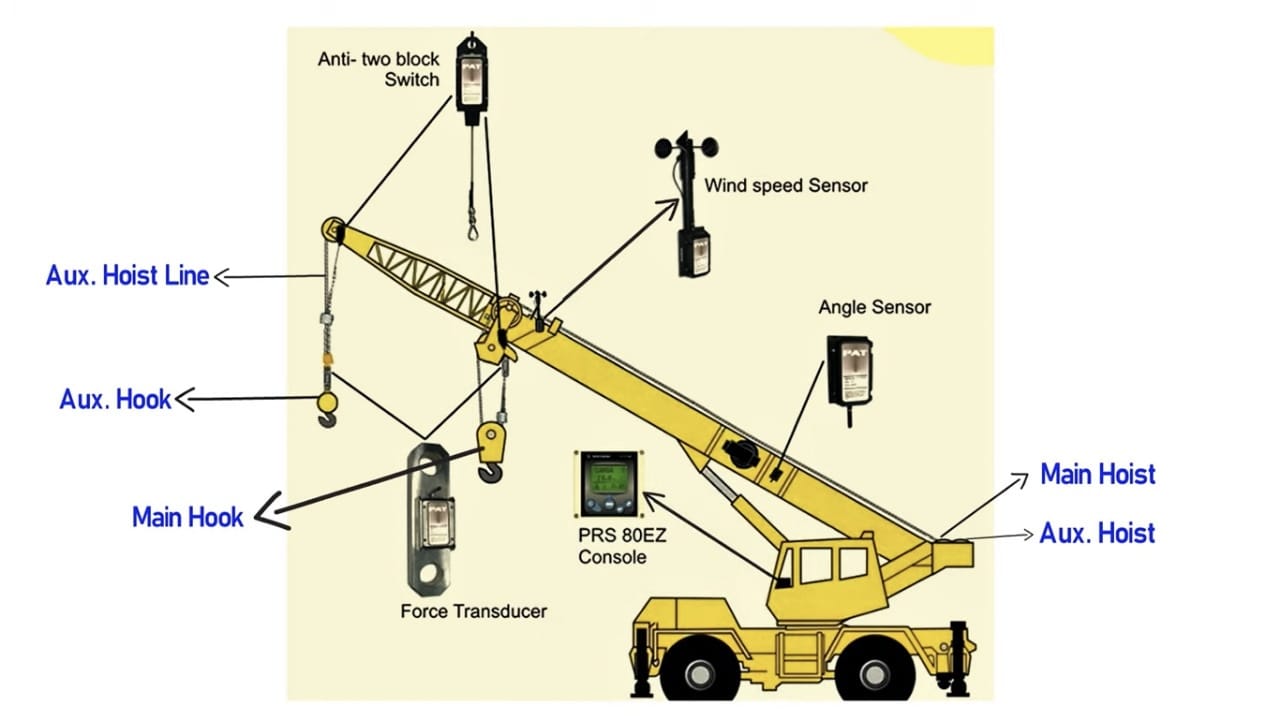
Further crane parts have been explained below:
1. Anti-Two Block Switch: This safety device is designed to prevent the hook block from colliding with the boom tip, which could cause damage or failure of the load line. It automatically stops the hoist when the hook block reaches a preset distance from the boom tip, ensuring safe crane operation.
2. Wind Speed Sensor: Monitors the current wind speed at the crane’s location. This is crucial for crane safety because high winds can affect the crane’s stability and the movement of the load. Operators rely on this data to determine whether conditions are safe for lifting operations.
3. Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the boom relative to the ground. This information is vital for calculating load charts, which help operators know the maximum safe lifting capacity at various angles and extensions of the boom.
4. Main Hoist: The primary lifting mechanism of the crane. It is responsible for lifting and lowering the main load line, which carries the primary lifting hook and load. It typically features a stronger motor and larger capacity compared to the auxiliary hoist.
5. Auxiliary Hoist: This secondary hoist is used for handling lighter loads or for dual hoisting operations where two separate loads are managed simultaneously. It operates independently of the main hoist and usually has its own hook and load line.
6. PRS 80EZ Console: This is an advanced control system or console used in cranes for better functionality and easier operation. It likely includes displays and controls for operating various crane functions, monitoring system status, and managing diagnostics.
7. Force Transducer: A sensor that measures the tension in the crane’s cables or structural stress during lifting operations. The data helps ensure that the crane operates within safe loading parameters, preventing structural overload.
8. Main Hook: Attached to the main hoist, this is the primary hook used for lifting heavy loads. It is designed to handle the maximum lifting capacity of the crane.
9. Aux Hook: Smaller than the main hook, the auxiliary hook is attached to the auxiliary hoist. It is used for lifting lighter loads and allows for more delicate or precise operations.
10. Aux Hoist Line: The cable or wire rope used with the auxiliary hoist. It is typically lighter and sometimes shorter than the main hoist line, suitable for smaller or secondary lifting tasks.
Understanding these components and their functions helps ensure safe and efficient crane operations, adapting to various operational needs and environmental conditions. Also, these parts work together to ensure that mobile cranes can perform a variety of lifting tasks efficiently and safely.